It is helpful for anyone who is in the brake parts business to understand how car brake systems work.
Understanding the brake system, you will know how to choose the best brake parts components and give professional suggestions to your customers.
In this article, we will break down the components, functions, and benefits that make up the braking system.
How the Brake System Works?
When you step on the brake pedal, it triggers the hydraulic system to move into action.
This system directs brake fluid through the brake lines and into the brake calipers, where it applies pressure to the brake caliper pistons.
The brake calipers then press the brake pads against the brake discs, creating the friction needed to reduce the vehicle’s speed or bring it to a halt.
The brake system is more than just a collection of components; it’s a carefully engineered system that converts the vehicle’s motion into heat, ensuring the vehicle can be safely controlled and stopped.
Types of Braking Systems
Disc Brakes
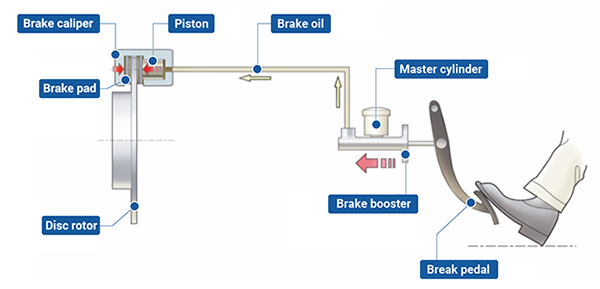
Components: Mainly include brake discs, brake pads, brake calipers, etc.
Function: When you depress the brake pedal, the hydraulic pressure is transmitted to the brake caliper, which pushes the piston or mechanical device to squeeze the brake pads against the brake disk, thus generating friction to slow down the wheel until it stops.
Benefits: Disc brakes are widely used in modern automobiles because of their advantages such as good heat dissipation, stable braking torque, and easy maintenance.
Drum Brakes
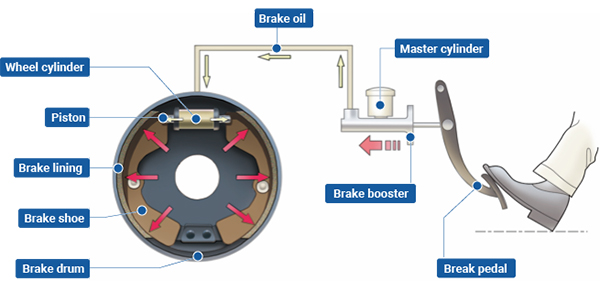
Components: Mainly including brake drum, brake shoe, brake parting pump, etc.
Function: When the driver depresses the brake pedal, the hydraulic or mechanical force pushes the brake shoes to expand outward, pressing against the inner surface of the brake drum, and decelerating the wheels through friction.
Benefits: Drum brakes are relatively simple in structure and low in cost, but they are not as good as disk brakes in terms of heat dissipation and braking torque stability, so they are mostly used in modern automobiles for rear-wheel or low-cost models.
ABS (Anti-lock Braking System)
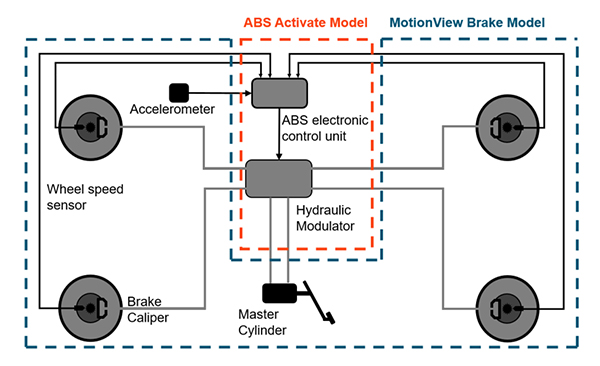
Components: The ABS is based on a conventional braking system with the addition of components such as sensors (to monitor wheel speed), controllers (to analyze sensor data and control brake pressure), and actuators (to regulate brake pressure).
Function: When the sensor detects that the wheels are about to lock, the controller will quickly adjust the braking pressure to keep the wheels in a state of imminent lock but not complete lock, thus ensuring the safety and maneuverability of the vehicle.
Benefits: The main purpose of the ABS is to prevent the wheels from locking up during emergency braking and to maintain the steering ability and stability of the vehicle.
Regenerative Braking
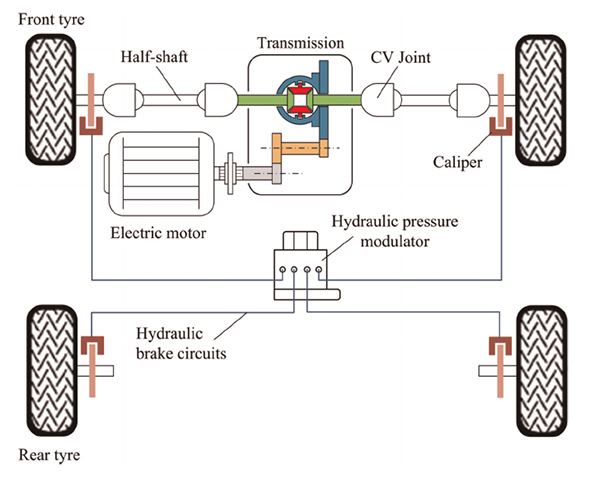
Components: In electric and hybrid vehicles, regenerative braking systems primarily use electric motors, batteries, and inverters.
Function: As the vehicle decelerates, the electric motor generates electricity from the kinetic energy, which is then stored in the battery for later use.
Benefits: This braking method not only enhances the vehicle’s energy efficiency but also contributes to extending its driving range, making it a key technology in modern electric and hybrid vehicles.
Conclusion
In summary, the brake system is a critical safety feature in any vehicle, transforming kinetic energy into heat energy through friction.
For those in the brake parts business, understanding this system is essential for selecting the right brake components and ensuring optimal performance.
When purchasing or recommending brake parts, consider the quality and function of each component to maintain safety and efficiency.
If you need brake parts, you can check GDST web which can supply high-quality brake parts at competitive prices for you.



